|
|
Core Transcriptional Regulatory Circuitry in Human Embryonic Stem Cells
Acknowledgements References |
To automatically determine bound regions in the datasets, we developed an algorithm to incorporate information from neighboring probes. For each 60-mer, we calculated the average X score of the 60-mer and its two immediate neighbors. If a feature was flagged as abnormal during scanning, we assumed it gave a neutral contribution to the average X score. Similarly, if an adjacent feature was beyond a reasonable distance from the probe (1000 bp), we assumed it gave a neutral contribution to the average X score. The distance threshold of 1000 bp was determined based on the maximum size of labeled DNA fragments put into the hybridization. Since the maximum fragment size was approximately 550 bp, we reasoned that probes separated by 1000 or more bp would not be able to contribute reliable information about a binding event halfway between them. This set of averaged values gave us a new distribution that was subsequently used to calculate p-values of average X (probe set p-values). If the probe set p-value was less than 0.001, the three probes were marked as potentially bound. As most probes were spaced within the resolution limit of chromatin immunoprecipitation, we next required that multiple probes in the probe set provide evidence of a binding event. Candidate bound probe sets were required to pass one of two additional filters: two of the three probes in a probe set must each have single probe p-values < 0.005 or the center probe in the probe set has a single probe p-value < 0.001 and one of the flanking probes has a single point p-value < 0.1. These two filters cover situations where a binding event occurs midway between two probes and each weakly detects the event or where a binding event occurs very close to one probe and is very weakly detected by a neighboring probe. Individual probe sets that passed these criteria and were spaced closely together were collapsed into bound regions if the center probes of the probe sets were within 1000 bp of each other. Regions of the Genome Bound By Oct4 (Table S1)Regions of the Genome Bound By Sox2 (Table S3) Regions of the Genome Bound By Nanog (Table S4) Regions of the Genome Bound By E2F4 (Table S6)
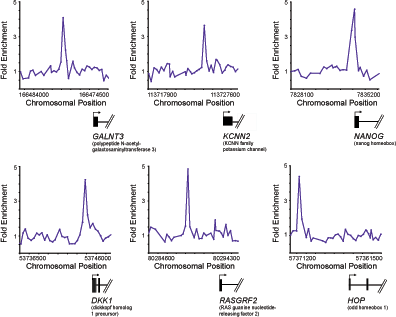
Figure 1b. Genome-wide ChIP-Chip in human embryonic stem cells Examples of Oct4 bound regions. Plots display unprocessed ChIP-enrichment ratios for all probes within a genomic region. Genes are shown to scale below plots (exons and introns are represented by thick vertical and horizontal lines, respectively), and the genomic region represented is indicated beneath the plot. The transcription start site and transcript direction are denoted by arrows. |
| YOUNG
LAB
Whitehead Institute 9 Cambridge Center Cambridge, MA 02142 [T] 617.258.5218 [F] 617.258.0376 CONTACT US |