|
|
Core Transcriptional Regulatory Circuitry in Human Embryonic Stem Cells
Acknowledgements References |
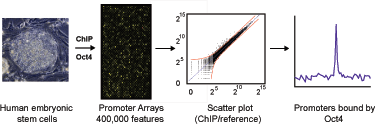
DNA sequences occupied by master regulators in ES cells were enriched using chromatin-immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and identified with a set of 10 arrays containing 400,000 unique spanning over 20,000 annotated transcription start sites from8kb upstream to 2kb downstream. This webpage describes the ChIP-chip protocol and microarray technology used in this experiment.
Figure 1a. Genome-wide ChIP-Chip in human embryonic stem cells. DNA segments bound by transcriptional regulators were identified using chromatin-immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and identified with DNA microarrays containing 60-mer oligonucleotide probes covering the region from -8kb to +2kb relative to the transcript start sites for 18,002 annotated human genes. ES cell growth and quality control, ChIP protocol, DNA microarray probe design and data analysis methods are described in detail in Experimental Procedures and Supplemental Data. AntibodiesChromatin Immunoprecipitations Microarray Design |
| YOUNG
LAB
Whitehead Institute 9 Cambridge Center Cambridge, MA 02142 [T] 617.258.5218 [F] 617.258.0376 CONTACT US |